9 heart Conditions – Asim Hameedi, MD
Heart is the most vital organ of the human body. Human body requires oxygenated blood to survive – and the heart is the main organ that controls the oxygenated blood supply from the lungs to other organs and systems. However, unhealthy habits and sedentary lifestyle gives rise to many heart abnormalities and diseases.
Several of these problems fall into the category of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, heart diseases encompass a comprehensive list of cardiovascular problems. However, cardiac abnormalities and seizures are the most common and leading causes of death among US citizens. Although the country is blessed with top cardiologists like Dr. Asim Hameedi, still heart seizure is the major cause, that 610,000 people in the country lose the battle of life every year.
Some of these diseases can be easily treated by interventional cardiology – without taking the risk of open-heart surgeries. However, the conditions treated by using non-surgical or interventional cardiology usually help the most common heart issues such as listed below:
9 Most Common Heart Conditions and their Signs & Symptoms
General cardiac issues like cholesterol build-up, increased level of cholesterol and excess calories can be easily controlled by exercise and treated by standard medical care. But, some heart conditions can be serious and need immediate medical attention. Following are the most common heart issues:
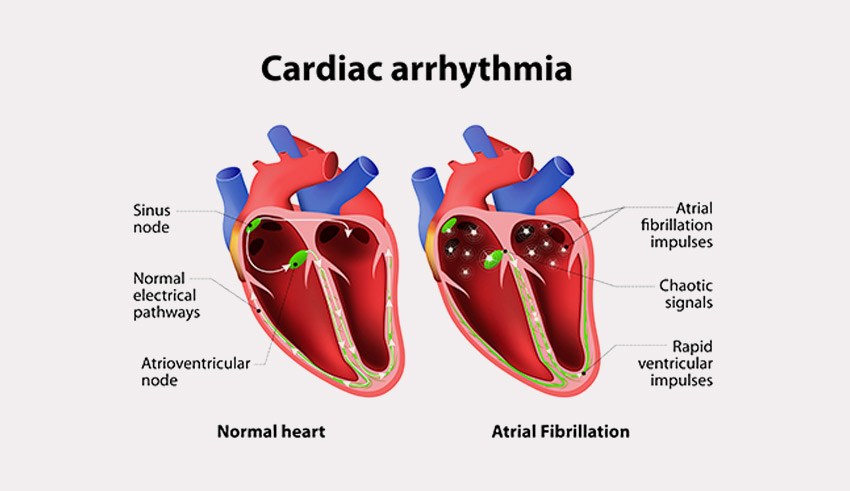
1. Arrhythmia – The Mild Condition
The heart condition or disorder highly affecting the heart rhythm of the human body is called Arrhythmia. It usually happens when the electric pulses that regulate heart disease do not function normally. This condition can be of the following types:
- Tachycardia – Abnormally Rapid Heartbeat
- Premature Contraction – Heart Contracts Earlier Than the Standard Time
- Fibrillation – Irregular Pattern of Breathing
- Bradycardia – Too Slow Heartbeat
Signs and Symptoms
Like every disorder, the signs and symptoms associated with the condition are:
- Rapid Heartbeat
- Feeling Like Your Heart Skipped a Beat
- Slow or Irregular Heartbeat
- Fatigue
- Excess Sweating
- Weakness
- Unconsciousness
- Dizziness
- Lightheartedness
- Mild or Severe Chest Pain
- Difficulty in Breathing
- Palpitations
- A Pounding Feeling in Your Neck or Chest
- Angina
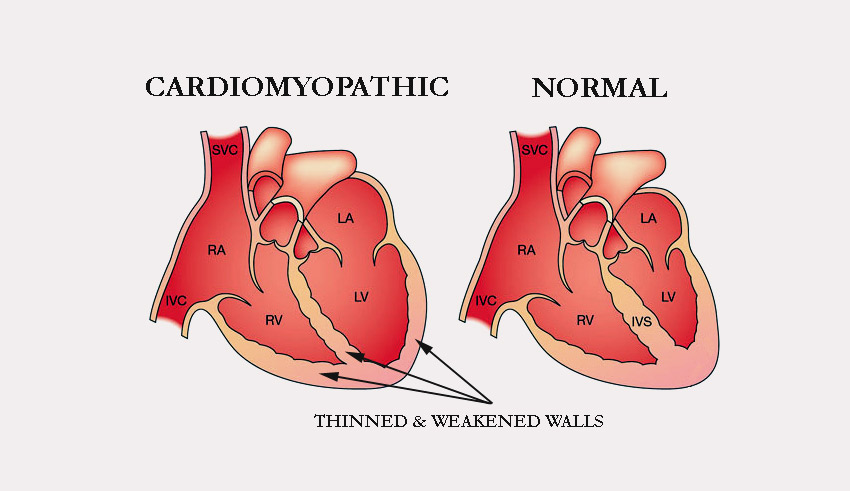
2. Cardiomyopathy – Enlargement of Heart
The condition is followed by the weakening of the heart resulting in heavy breathing and shortness of breath. It is critical to diagnose the seriousness of the condition asap, as it can be fatal if not treated on time.
However, in some patients, the condition appears to be converted from cardiomyopathy to dilated cardiomyopathy. According to medical evidence, this condition is fatal and has already taken the lives of millions of people around the globe.
Signs and Symptoms
- Unusual sounds are produced by the heart, referred to as heart murmurs.
- Fatigue
- Arrhythmia
- Swelling in different organs like the ankle, abdomen and veins, etc.
- Trouble breathing
- Chest Pain – Angina
- Dizziness
- Lightheartedness
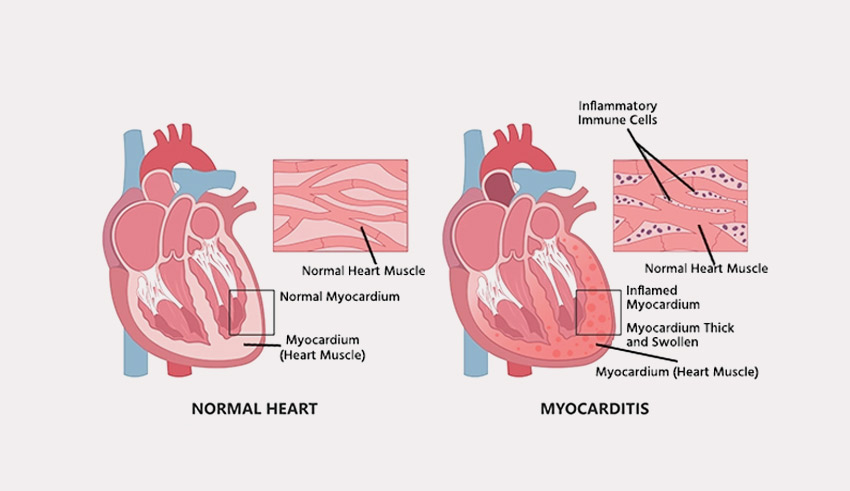
3. Myocarditis – Inflammation of Heart Muscles
Heart muscles are elastic and strong enough to bear the pressure of the blood flowing day and night in the body. However, for various reasons, inflammation is sometimes caused in the heart myocardium – the muscle layer of the heart that pumps the blood actively within the body. Such a condition of heart muscle inflammation is called myocarditis.
Signs and Symptoms
- Sharp Stabbing Chest Pain
- Abnormal Heartbeat – Arrhythmia
- Loss of Consciousness
- Fatigue
- Sharp Aching Waves in The Shoulder
- Chest Inflammation
In severe cases, the condition becomes chronic, leading to the enlarged heart condition known as – dilated cardiomyopathy. Here the patient may exhibit slightly different symptoms:
- Fever
- Severe Headache
- Aching of The Muscles
- Sore Throat
- Diarrhea
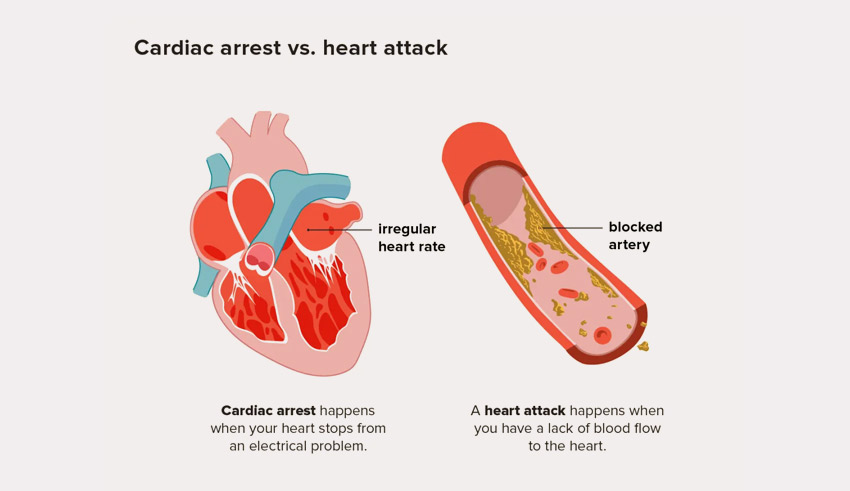
4. Cardiopulmonary Arrest – Heart Attack
A heart attack is a sudden loss of heart function. The condition is also known as cardiopulmonary arrest, which is the most common cause of death around the world. Every year, a considerable population is deducted from the global population due to the death caused by sudden cardiac arrest. However, the condition results from the abnormal or dysfunction of the electrical system of the cardiovascular system.
Cardiac arrest is quite different from a heart attack as the causes of both conditions are entirely different. On the contrary, heart attack causes some severe disturbance in the heart’s electrical system, which leads to sudden cardiac arrest and may cause death if not given immediate medical assistance.
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are sudden, drastic and can be extremely fatal at times. Some of the significant symptoms include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Sudden Collapse
- Pulse Arrest
- No Breathing
- Chest Discomfort
- Heart Palpitations
- Fainting or Dizziness
- Shortness of Breath
- Unusual Wheezing
However, under the conditions where the patient faces heart palpitation, immediate medical care and assistance can save his life.
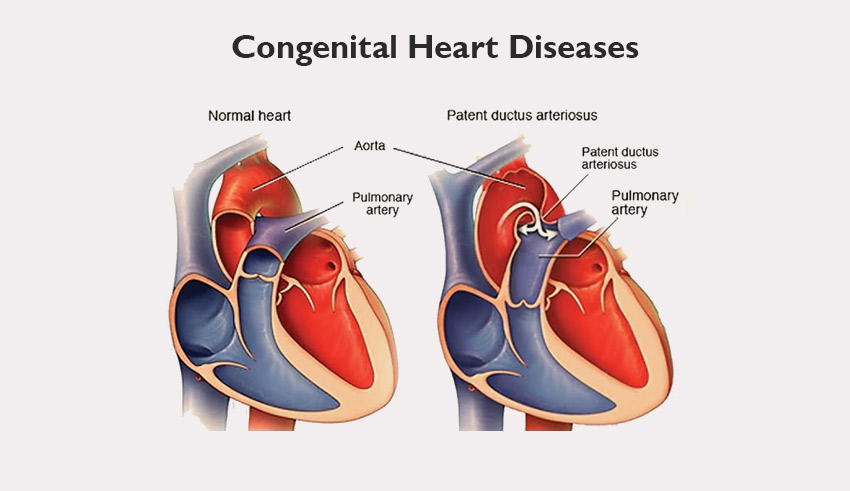
5. Congenital Heart Diseases – By Birth Heart Defects
One of the critical reasons for heart defects and abnormalities is that the heart is weak or perforated by birth. However, congenital diseases are pretty much common in the UK and USA, where every 1 out 100 babies are diagnosed suffering from congenital heart disease.
However, the diagnostic time of the conditions is not fixed. In many cases, the disorder or abnormal functionality is diagnosed before birth, in some cases during childhood or after growing up.
Types of Congenital Diseases
Three conditions of congenital heart diseases are:
- Atresia – One Heart Valve Missing or Undeveloped
- Septal Defects – A Hole in The Heart Walls, Either The Upper Chambers or The Lower Chambers
- Atypical Heart Vessels – The Valves May Not Open Properly or May Cause Blood Leakage
As a matter of fact, there are no specified causes of congenital heart diseases, but one of the most observed causes includes Down Syndrome – A genetic disorder that affects or stops the cardiovascular development of the fetus.
Signs and Symptoms
Congenital heart diseases have several symptoms, particularly in children and adults. However, these symptoms include:
- Cyanosis – blue tinge appears on skin and lips
- Rapid Heartbeat
- Swelling on the belly and ankles
- Rapid breathing
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Endocarditis
- Problems in the heart rhythm
- Clotting of the blood
- Failure or Dysfunction of the heart
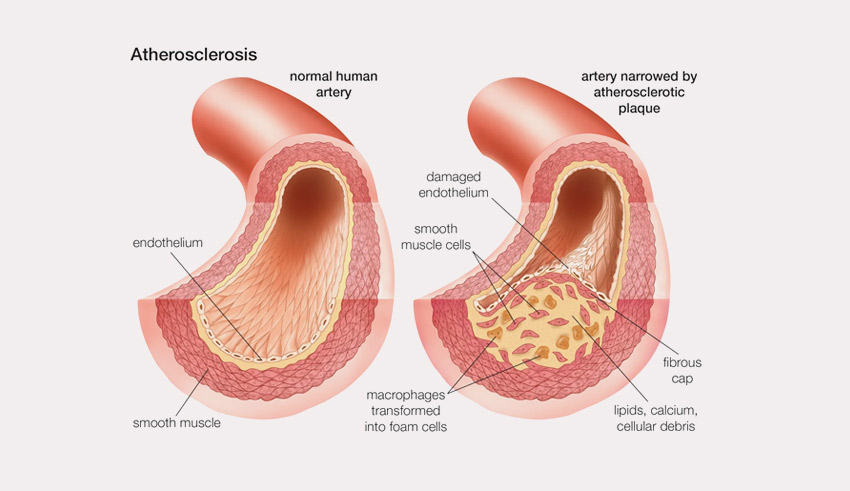
6. Atherosclerosis – Narrowing of Arteries
The narrowing of the arteries due to the accumulation of plaque is known as atherosclerosis. Plaque is a combination of fats, cholesterol, blood elements, and calcium that stick to the walls of the heart – disturbing the functionality of the cardiovascular system.
However, arteries and veins are the essential blood vessels of the heart which maintain the blood flow of the heart. However, plaque build-up in the body or around the heart can be really dangerous for the cardiovascular system. The most observed symptoms of the disease are grouped below:
Signs and Symptoms
- Claudication – Leg pain while walking
- Angina – Chest Pain
- Increased Blood Pressure
- Signs of Kidney Failure
- Arrhythmia – Irregular Heartbeat
- Impaired Vision
- Sudden & Severe Headache
- Loss of Consciousness
- Trouble Speaking
- Difficulty Breathing
- Nausea
- Loss of Appetite (Some cases)
- Frequent Urination
- Ground Itching
However, the severity of the condition strictly depends on the type of affected blood vessels. In case of early diagnosis, the condition can be prevented from being severe and fatal.
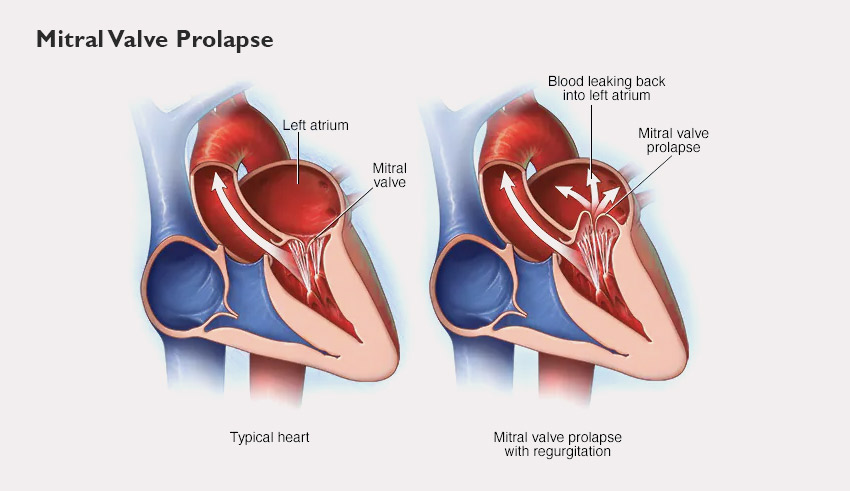
7. Mitral Valve Prolapse – Click Murmur Syndrome
The bulging of one or more mitral valve flaps into the left atrium during the contraction of the heart is called mitral valve prolapse. However, the disease is also termed as Barlow’s Syndrome, Balloon Mitral Valve, Floppy Valve Syndromes.
The Click Murmur Syndrome was given this name because of the murmuring sound produced by the turbulent blood flow. However, the cause of the disease is still unknown, but it is observed to be hereditary in most cases.
Signs and Symptoms
Mitral valve prolapse may or may not show symptoms. But, like every heart condition, this condition is also has symptoms that are common in most case. On the contrary, the severe symptoms may vary according to the degree of prolapse from person to person. Common symptoms are:
- Palpitations – Burst of Rapid heart beats
- Severe Chest Pain
- Mitral Regurgitation – Enlargement of Left Atrium/Left Ventricle
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Shortness of Breath
- Irregular Heartbeat
- Anxiety
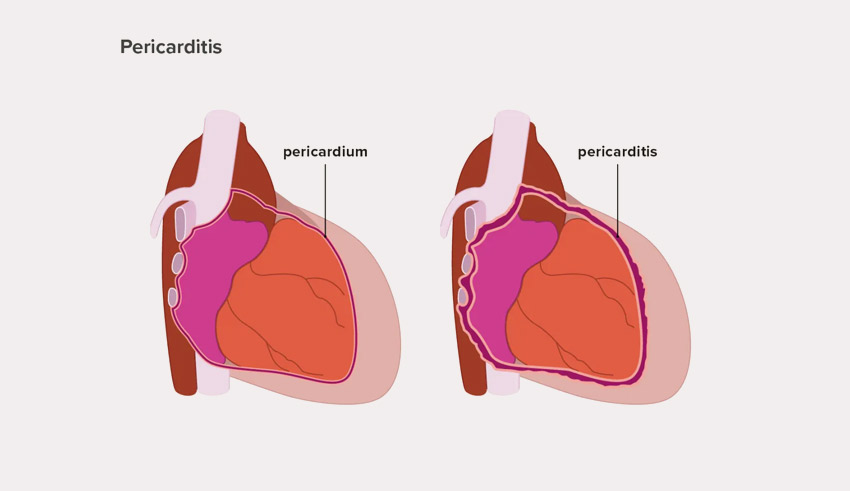
8. Pericarditis – Inflammation of The Pericardial Layer
The pericardium is the thin fibroblastic sac around the heart, which is composed of two distinct layers. When any one layer of the pericardium causes inflammation, the condition is known as pericarditis.
The space between the pericardial layers contains pericardial fluid. However, if the pericardium is damaged or perforated, it may lead to the production of excess fluid. Pericarditis may be acute or chronic, depending upon the severity.
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of the conditions are almost similar to the other heart condition, but there may be some severe symptoms as well:
- Chest Pain – On the left side of the chest
- Cough
- Abdominal Pain
- Swelling of the legs
- Low-grade fever
- Pounding or racing heart
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Nausea
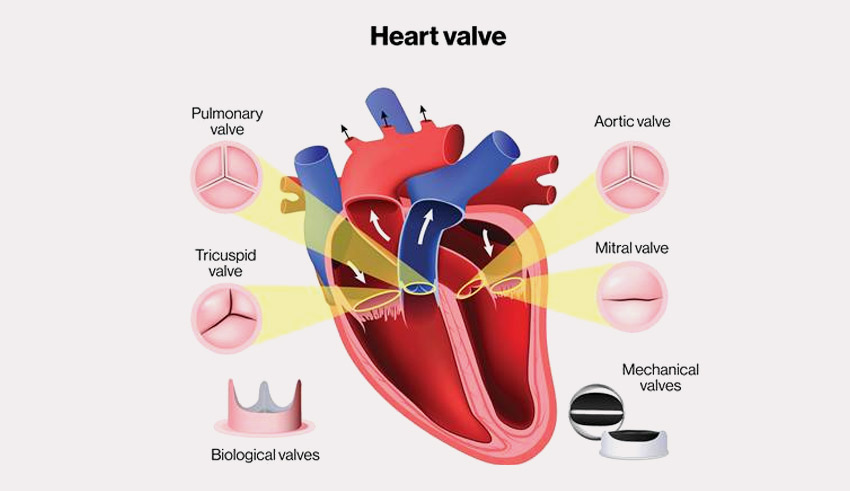
9. Valvular Heart Disease – Damage of The Valves of the Heart
The human heart contains four main valves whose opening, closing and proper functioning manage the blood flow within the human body. The four essential valves of the heart are as follows:
- Aortic Valve – Controls the blood flow from the heart to the body. However, the diseased condition of the aortic valve is known as Aortic Valve Stenosis. The condition may be fatal.
- Mitral valve – The Valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle, which regulates the blood flow from the upper left chamber into the lower left chamber. The diseased condition of the valve is termed as the Mitral Valve Prolapse.
- Pulmonary Valve – Also known as the pulmonary valve. It is a heart valve that lies between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle. The diseased condition of the valve is termed as Pulmonary Valve Stenosis.
- Tricuspid Valve – The valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle is known as the Tricuspid valve. The diseased condition of the valve is termed as Tricuspid Stenosis.
Diagnostic Methods
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).An ECG is a quick and painless test that records the electrical signals in your heart. It can spot abnormal heart rhythms. You may have an ECG while you’re at rest or while exercising (stress electrocardiogram).
- Holter monitoring: A Holter monitor is a portable ECG device you wear to continuously record your heart rhythm, usually for 24 to 72 hours. Holter monitoring is used to detect heart rhythm problems that aren’t found during a regular ECG exam.
- Echocardiogram: This noninvasive exam uses sound waves to produce detailed images of your heart’s structure. It shows how your heart beats and pumps blood.
- Stress test: This type of test involves raising your heart rate with exercise or medicine while performing heart tests and imaging to check how your heart responds.
- Cardiac catheterization: In this test, a short tube (sheath) is inserted into a vein or artery in your leg (groin) or arm. A hollow, flexible and longer tube (guide catheter) is then inserted into the sheath. Using X-ray images on a monitor as a guide, your doctor carefully threads the catheter through the artery until it reaches your heart. During cardiac catheterization, the pressures in your heart chambers can be measured, and dye can be injected. The dye can be seen on an X-ray, which helps your doctor see the blood flow through your heart, blood vessels and valves to check for problems.
- Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan: In a cardiac CT scan, you lie on a table inside a doughnut-shaped machine. An X-ray tube inside the machine rotates around your body and collects images of your heart and chest.
- Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): A cardiac MRI uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of your heart.
You can visit for more details.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353124
Treatments & Medications
Some of the non-invasive or interventional cardiology treatments are as follows.
Angioplasty
One of the most common methods of heart treatment is Angioplasty. Angioplasty is used for the treatment of the obstructed coronary artery that is damaged due to the coronary disease. The angioplasty is followed by the insertion of a deflated balloon catheter into the damaged artery to relieve the narrowing of the artery.
However, to keep the damaged artery open and functioning, certain devices like coronary stents are deployed within the obstructed artery. In case of a heart attack, the angioplasty is restricted to the obstructed artery – the one that caused the heart attack.
Like every disease, heart diseases must be treated with or without medicines depending on the severity of the condition. Apart from non-invasive cardiology and catheterization, heart conditions can also be controlled by medications. Some medication classes are:
Anticoagulants
These medications that prevent the blood from clotting are known as the blood anticoagulants. However, the anticoagulants are also known as the blood thinners. Sometimes these medications are given to the patient through oral means.
Beta Blockers
Increased heart rate can cause heart failure or seizure leading to the death of the patient. However, before making the patient an aim of the surgical tools the cardiologists go for the drug treatment. The beta blockers are proven to reduce the blood pressure and the heart rate, decreasing the risk of myocardial failure.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Controlling the blood pressure can prevent the arrhythmia – abnormal heartbeat. Medicines like Cardizem are calcium channel blockers that can lower the blood pressure of the patient by decreasing the blood pumping strength of the heart.
Diuretics
The patients suffering from heart disorders can be in grave danger if the workload on their heart is increased. To control the workload on the heart, diuretics are prescribed to the patient that helps reduce the heart’s pumping load. Also, it removes the excess water from the body.
Vasodilators
Relaxing the blood vessels is the most essential thing to prevent the risk of heart diseases. However, the body of a cardiac patient cannot relax the blood vessels naturally. These vasodilators are prescribed to such patients that relaxes the blood vessels, minimizing the risk of cardiac arrest.
10 Ways to Improve Your Health Permanently
Heart health can be improved in a number of ways, but doing it in a natural way would be better than taking heavy doses of medications. Here are some ways to have a healthy heart:
- Exercise
- Healthy Diet
- Dark Chocolate
- Lose Belly fat
- Stop Smoking
- Avoid Alcohol
- Control your Blood Pressure
- Control your Diabetes
- Avoid Stress
- Lower your Cholesterol
Conclusion
Healthy life style takes effort and commitment. Heart diseases can be fatal if not intervened on time. However, there are many other methods in non-invasive cardiology to improve heart health. Also, there are many interventional cardiologists like Dr. Asim Hameedi, who are experts in treating the patients, without surgery.
